Your React site must be accessible to be progressive. Audit for accessibility during development to find and address any issues before you push your application into production.
react-axe is a library that audits a
React application and logs any accessibility issues to the Chrome DevTools
console. It uses the open-source axe
testing library to flag any issues and their severity.
eslint-plugin-jsx-a11y is
an ESLint plugin that identifies and enforces a number of accessibility rules
directly in your JSX. When used in combination with a tool that tests the final
rendered DOM, such as react-axe, you can find and fix any accessibility
concerns on your site.
Why is this useful?
It's crucial to build websites that are accessible to all users, including those
with disabilities. By using an accessibility audit library, such as
react-axe and eslint-plugin-jsx-a11y, you can find accessibility issues as
you build your application, so you can fix them before going to production.
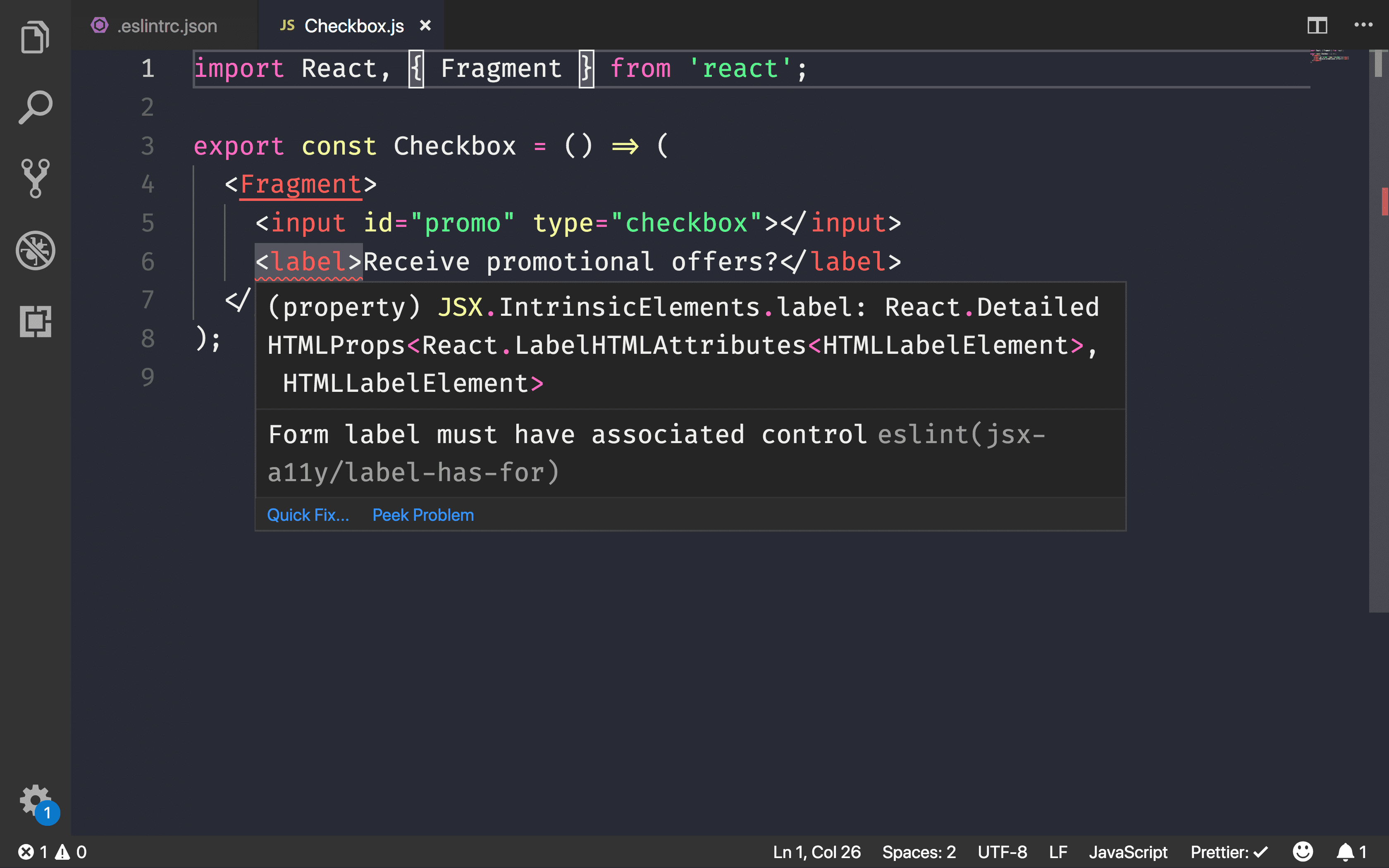
Use eslint-plugin-jsx-a11y
React already supports writing accessible HTML elements within JSX syntax. For
example, use the htmlFor attribute instead of for to add a label to a
form element within a React component.
<input id="promo" type="checkbox">
<label htmlFor="promo">Receive promotional offers?</label>
The
React accessibility documentation
covers the nuances of handling accessibility concerns within a React
component. To more easily spot these issues, Create React App (CRA) includes
the eslint-plugin-jsx-a11y plugin.
To enable pre-configured linting provided by CRA:
- Install the ESLint plugin for your code editor.
- Add a
.eslintrc.jsonfile to your project
{
"extends": "react-app"
}
Once configured, common accessibility issues can be found.
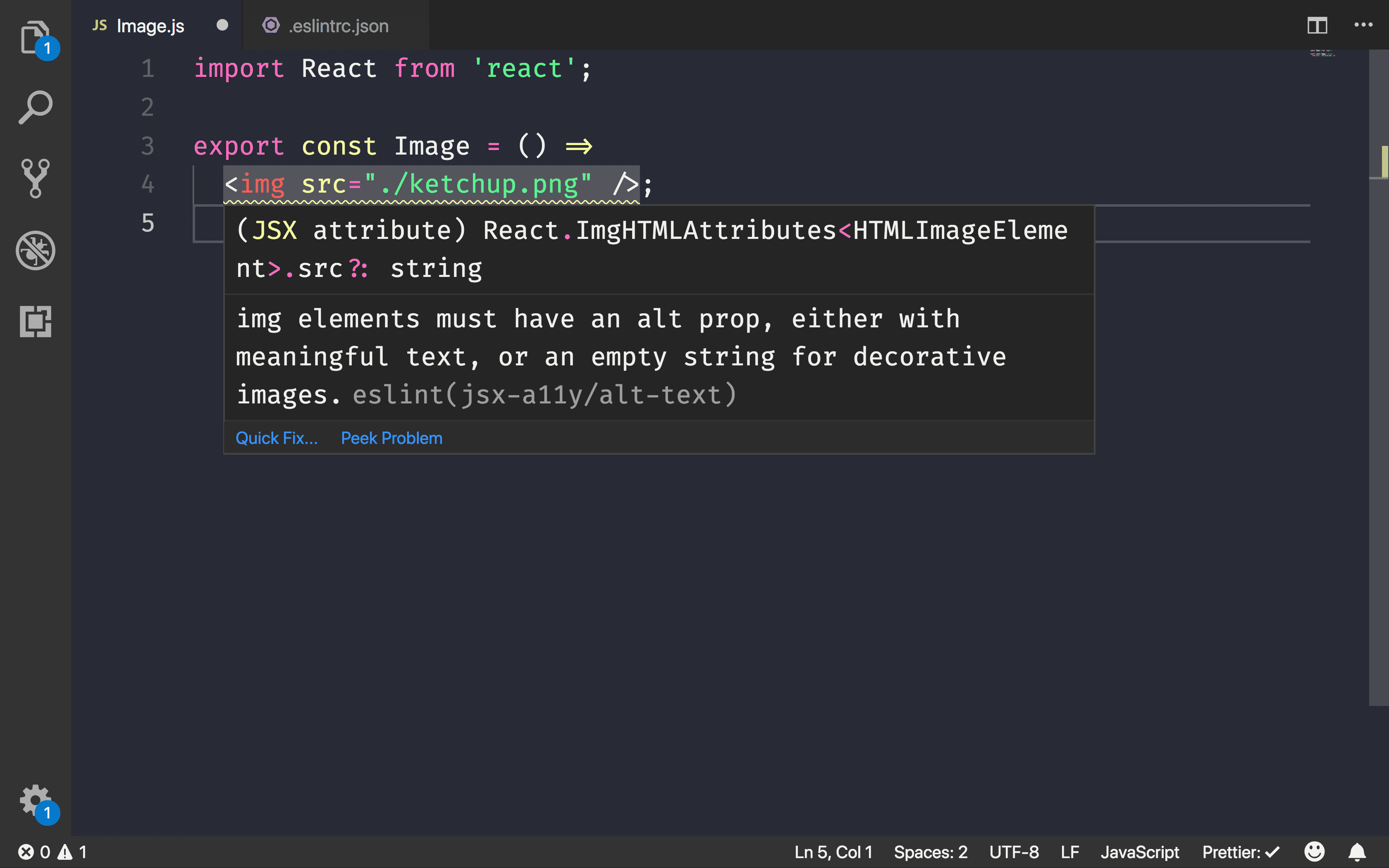
To check for more accessibility rules, modify .eslintrc.json to include all of
the plugin's recommended rules:
{
"extends": ["react-app", "plugin:jsx-a11y/recommended"]
}
For an even stricter subset of rules, switch to strict mode:
{
"extends": ["react-app", "plugin:jsx-a11y/strict"]
}
The project documentation provides information on the differences between recommended and strict mode.
Use react-axe
eslint-plugin-jsx-a11y can help you find any accessibility issues in your JSX,
but it does not test any of the final HTML output. The react-axe library
conducts testing by adding a React wrapper around the
axe-core testing tool by Deque Labs.
- Install the library as a development dependency:
bash npm install --save-dev react-axe - Initialize the module in
index.js:js if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { import('react-axe').then(axe => { axe.default(React, ReactDOM, 1000); ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root')); }); } else { ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('root')); }
A dynamic import loads the library,
as long as it's not in production, before rendering and booting up the root
App component. This ensures that the it's not included in the final
production bundle if it's unnecessary.
When you run the application during development, issues are surfaced directly to the Chrome DevTools console.
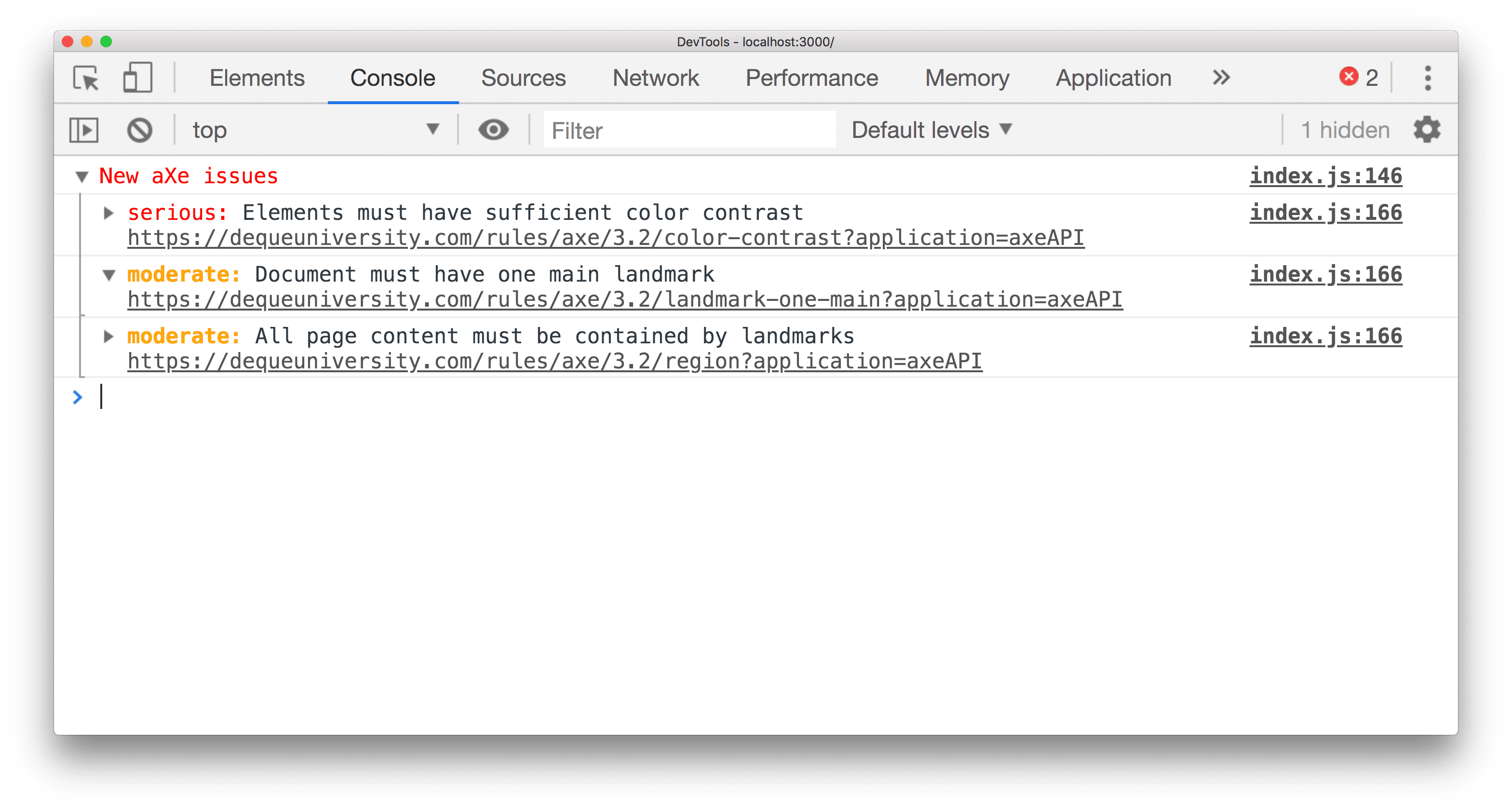
A severity level is also assigned for each violation. These levels are:
- Minor
- Moderate
- Serious
- Critical
Conclusion
Include accessibility audits early in your workflow to catch problems as you
build your React applications.Use eslint-plugin-jsx-a11y to add accessibility
checks into your linting workflow. CRA already includes it, but you can switch
to either the recommended or strict mode.
In addition to local development testing, include react-axe in your
application to catch any issues on the final rendered DOM. Don't include it
into your production bundle.

