Before you build with AI, you have to choose the platform it's hosted on. Your choice impacts the speed, cost, scalability, and trustworthiness of your AI system. You can choose between:
- Client-side AI: Runs directly in the browser. This means data can stay private, on the user's device, and there's no network latency. However, to perform well, client-side AI needs highly specific, well-defined use cases.
- Server-side AI: Runs in the cloud. It's highly capable and scalable, but more expensive in terms of latency and cost.
Each option comes with trade-offs, and the right setup depends on your use case, team skills, and resources. For example, you may offer a summarization tool that runs locally so users can ask personal questions without needing to manage personally identifiable information (PII). However, a customer support agent could give more useful answers by using a cloud-based model that has access to a large database of resources.
In this module, you learn how to:
- Compare the trade-offs between client and server-side AI.
- Match your platform to your use case and team capabilities.
- Design hybrid systems, which offer AI on the client and server, to grow with your product.
Review the options
For deployment, think of AI platforms along two primary axes. You can choose:
- Where the model runs: Is it running client-side or server-side?
- Customizability: How much control do you have over the model's knowledge and capabilities? If you can control the model, meaning you can modify the model weights, you can customize its behavior to meet your specific requirements.
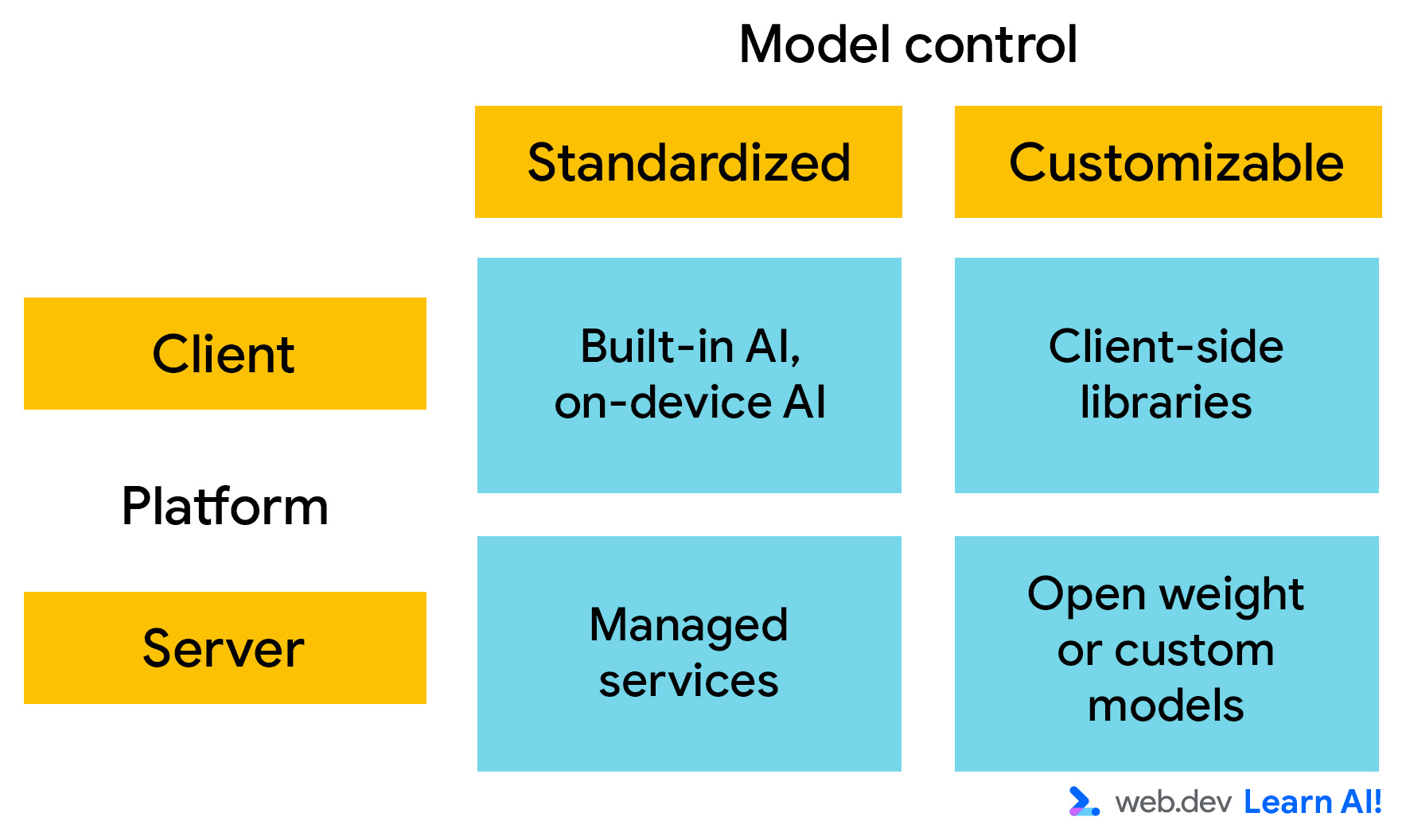
Client-side AI
Client-side AI runs in the browser, and computation happens locally on the user's device. You don't need to provide for inference-time compute, and data stays on the user's machine. This makes it fast, private, and suitable for lightweight, interactive experiences.
However, client-side models are usually quite small, which can constrain their capabilities and performance. They're best suited for highly specialized tasks, such as toxicity detection or sentiment analysis. Often, these are predictive AI tasks with a limited output space.
There are two primary options:
- Built-in AI: Browsers, such as Google Chrome and Microsoft Edge, are integrating AI models. These are accessible through JavaScript calls, with no setup or hosting required. Once the model is downloaded, it can be called by all websites that use it.
- Custom models: You can use client-side libraries, such as Transformers.js and MediaPipe, to integrate models into your application. This means you can control the model weights. However, that also means that every user of your website has to download your custom model. Even the smallest AI models are large in the context of a website.
Server-side AI
With server-side AI, your web application calls an API to send inputs to the AI model and receive its outputs. This setup supports larger, more complex models and is independent of user hardware.
The two categories for server-side AI are:
- Managed services: These are models hosted in data centers by a third-party, such as Gemini 3 and GPT-5. The model owner provides an API to access it. This means you can use state-of-the-art models with minimal setup. These are ideal for fast prototyping, open-ended conversation, and general-purpose reasoning. However, scaling on a managed service can be expensive.
- Self-hosted models: You can deploy open-weight models, such as Gemma or Llama, on your own infrastructure or in a managed container, such as Vertex AI or Hugging Face Inference. This approach means you can benefit from pre-training done by the model creator, but you maintain control over the model, fine-tuning data, and performance.
Choose an initial platform
Review the architectural characteristics of the AI platforms and analyze the trade-offs to decide on your initial setup.
Define your architectural requirements
With every decision, you have to make compromises. Take a look at the key characteristics that define the cost and value of your AI platform:
- Model power: How well the model performs across a wide range of users and tasks, without tuning. Often, this correlates with model size.
- Customizability: The extent to which you can fine-tune, modify, or control model behavior and architecture.
- Accuracy: The overall quality and reliability of the model's predictions or generations.
- Privacy: The degree to which user data stays local and under user control.
- Fixed cost: The recurring expense required to operate the AI system regardless of usage, incl. infrastructure provisioning and maintenance.
- Cost-per-request: The additional cost of each incoming request.
- Compatibility: How widely the approach works across browsers, devices, and environments without fallback logic.
- User convenience: Whether users need to take extra steps to use the AI system, like downloading a model.
- Developer convenience: How quick and easy it is to most developers to deploy, integrate, and maintain the model, without specialized AI expertise.
The following table provides an example of estimates for how well each platform performs for each criterion, where 1 is the lowest and 5 is the highest.
| Criteria | Client | Server | ||
| Built-in AI or on-device | Custom model | Managed service | Self-hosted model | |
| Model power |
Why 2 stars for model power?Built-in and on-device AI ues small, preloaded browser models optimized for narrow, task-specific features, rather than open-ended conversation or reasoning. |
Why 3 stars for model power?Custom client-side libraries offer more flexibility than built-in AI, but you're still constrained by download size, memory limits, and user hardware. |
Why 4 stars for model power?With managed services and self-hosting, you have access to large, state-of-the-art models, capable of complex reasoning, long context handling, and broad task coverage. |
|
| Customizability |
Why 1 star for customizability?Built-in models don't allow access to model weights or training data. The primary way to customize their behavior is through prompt engineering |
Why 5 stars for customizability?This option gives you control over model selection and weights. Many client-side libraries also allow for model fine-tuning and training. |
Why 1 star for customizability?Managed services expose powerful models but offer minimal control over their internal behavior. Customization is typically limited to prompting and input context. |
Why 5 stars for Customizability?Self-hosted models provide full control over model weights, training data, fine-tuning, and deployment configuration. |
| Accuracy |
Why 2 stars for accuracy?Accuracy in built-in models is sufficient for well-scoped tasks, but limited model size and generalization reduce reliability for complex or nuanced inputs. |
Why 3 stars for accuracy?Custom client-side model accuracy can be improved in the model selection process. However, it remains constrained by model size, quantization, and client hardware variability. |
Why 5 stars for accuracy?Managed services typically offer relatively high accuracy, benefiting from large models, extensive training data, and continuous provider improvements. |
Why 4 stars for accuracy?Accuracy can be high, but depends on the selected model and tuning effort. Performance may lag behind managed services. |
| Network latency |
Why 5 stars for network latency?Processing happens directly on the user's device. |
Why 2 stars for network latency?There's a roundtrip to a server. |
||
| Privacy |
Why 5 stars for privacy?User data should remain on the device by default, minimizing data exposure and simplifying privacy compliance. |
Why 2 stars for privacy?User inputs must be sent to external servers, increasing data exposure and compliance requirements. However, there are specific solutions to mitigate privacy issues, such as Private AI Compute. |
Why 3 stars for privacy?Data remains under your organizational control, but still leaves the user's device and requires secure handling and compliance measures. |
|
| Fixed cost |
Why 5 stars for fixed cost?Models run on users' existing devices, so there is no additional infrastructure cost. |
Why 5 stars for fixed cost?Most APIs charge based on usage, so there is no fixed cost. |
Why 2 stars for fixed cost?Fixed costs include infrastructure, maintenance, and operational overhead. |
|
| Cost-per-request |
Why 5 stars for cost-per-request?There is no per-request cost, as inference runs on the user's device. |
Why 2 stars for cost-per-request?Managed services tend to have per-request pricing. Scaling costs can become significant, especially at high traffic volumes. |
Why 3 stars for cost-per-request?No direct per-request cost; effective per-request cost depends on infrastructure utilization. |
|
| Compatibility |
Why 2 stars for compatibility?Availability varies by browser and device, requiring fallbacks for unsupported environments. |
Why 1 star for compatibility?Compatibility depends on hardware capabilities and runtime support, limiting reach across devices. |
Why 5 stars for compatibility?Server-side platforms are broadly compatible for all users, as inference happens server-side and clients only consume an API. |
|
| User convenience |
Why 3 stars for user convenience?It's generally seamless once available, but built-in AI requires an initial model download and browser support. |
Why 2 stars for user convenience?Users may encounter delays due to downloads or unsupported hardware. |
Why 4 stars for user convenience?Works immediately with no downloads or device requirements, providing a smooth user experience. However, there may be a lag if there's low network connection. |
|
| Developer convenience |
Why 5 stars for developer convenience?Built-in AI requires minimal setup, no infrastructure, and little AI expertise, making it easy to integrate and maintain. |
Why 2 stars for developer convenience?Requires managing models, runtimes, performance optimization, and compatibility across devices. |
Why 4 stars for developer convenience?Managed services simplify deployment and scaling. However, they still require API integration, cost management, and prompt engineering. |
Why 1 stars for developer convenience?A custom server-side deployment demands significant expertise in infrastructure, model management, monitoring, and optimization. |
| Maintenance effort |
Why 4 stars for maintenance effort?Browsers handle model updates and optimization, but developers must adapt to changing availability. |
Why 2 stars for maintenance effort?Requires ongoing updates for models, performance tuning, and compatibility as browsers and devices evolve. |
Why 5 stars for maintenance effort?Maintenance is handled by the provider. |
Why 2 stars for maintenance effort?Requires continuous maintenance, including model updates, infrastructure management, scaling, and security. |
Analyze trade-offs
To illustrate the decision-making process, we'll add another feature to Example Shoppe, a mid-sized ecommerce platform. You're interested in saving costs in off-hours customer service, so you decide to build an AI-powered assistant to answer user questions about orders, returns, and products.
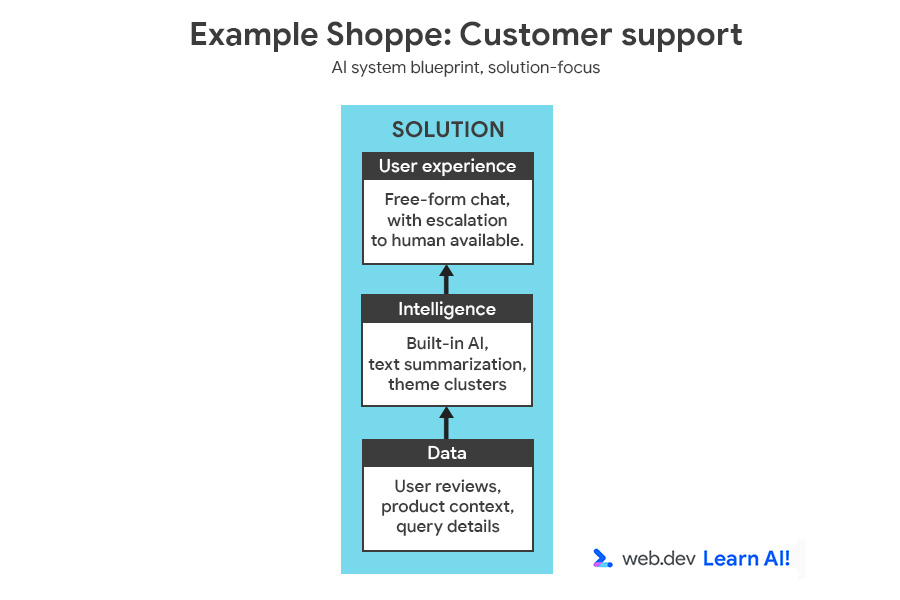
You can review the full AI system blueprint, featuring the opportunity and solution.
Analyze the scenario using two lenses: use case requirements and business or team constraints.
| Requirement | Analysis | Criteria | Implication |
| High accuracy and versatility | Users ask a variety of complex questions about orders, products, and returns. | Model power, accuracy | Requires a large language model (LLM). |
| Data specificity | It needs to answer questions specific to company data, products, and policies. | Customizability | Requires data ingestion, such as RAG, but not model fine-tuning. |
| Requirement | Analysis | Criteria | Implication |
| User base | Hundreds of thousands of users. | Scalability, compatibility | Requires an architecture that handles high, reliable traffic. |
| Post-launch focus | Team will move to other projects after version 1 launches. | Maintenance effort | Need a solution with minimal ongoing maintenance. |
| Team expertise | Strong web developers, limited AI/ML expertise | Developer convenience | Solution must be easy to deploy and integrate without specialized AI skills. |
Now that you've prioritized your criteria, you can refer to the trade-off estimation table to determine what platform matches your highest-priority criteria:
It's clear from this breakdown that you should use server-side AI, and probably a managed service. This offers a versatile model for complex customer questions. It minimizes maintenance and development effort by offloading infrastructure, model quality, and uptime to the provider.
While customizability is limited, this is a worthwhile trade-off for a web development team with limited model engineering experience.
A retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) setup can help you to provide the relevant context to the model at inference time.
Hybrid AI
Mature AI systems rarely run on a single platform or with one model. Rather, they distribute AI workloads to optimize the trade-offs.
Spot opportunities for hybrid AI
Once you've launched, you should refine your requirements based on real-life data and feedback. In our example, Example Shoppe, you wait a few months to analyze the results and find the following:
- Around 80% of requests are repetitive ("Where is my order?", "How do I return this?"). Sending these requests to a managed service creates a lot of overhead and cost.
- Only 20% of requests require deeper reasoning and an open-ended, interactive conversation.
A lightweight local model could classify user inputs and answer routine queries, such as, "What is your return policy?" You can route complex, rare, or ambiguous questions to the server-side model.
By implementing both server-side and client-side AI, you can reduce costs and latency, while maintaining access to powerful reasoning when needed.
Distribute the workload
To build this hybrid system for Example Shoppe, you should start by defining the default system. In this case, it's best to start client-side. The application should route to server-side AI in two cases:
- Compatibility-based fallback: If the user's device or browser cannot handle the request, it should fall back to the server
- Capability-based escalation: If the request is too complex or open-ended for the client-side model, as defined by predetermined criteria, it should be escalated to a larger server-side model. You could use a model to classify the request as common, so you perform the task client-side, or uncommon, and you send the request to the server-side system. For example, if the client-side model determines that the question is related to an uncommon issue, such as getting a refund in a different currency.
Flexibility introduces more complexity
Distributing workloads between two platforms makes you more flexible, but it also adds complexity:
- Orchestration: Two execution environments mean more moving parts. You need logic for routing, retries, and fallbacks.
- Versioning: If you use the same model across platforms, it must stay compatible across both environments.
- Prompt engineering and context engineering: If you use different models on each platform, you need to perform prompt engineering for each.
- Monitoring: Logs and metrics are split and require extra unification effort.
- Security: You're maintaining two attack surfaces. Both local and cloud endpoints need hardening.
This is another trade-off for your consideration. If you have a small team or you're building a non-essential feature, you may not want to add this complexity.
Your takeaways
Expect your platform choice to evolve. Start from the use case, align with your team's experience and resources, and iterate as both your product and your AI maturity grow. Your task is to find the right mix of speed, privacy, and control for your users, then build with some flexibility. This way, you can adapt to changing requirements and benefit from future platform and model updates.
Resources
- As platform and model choice is interdependent, read more about model selection.
- Read how to go beyond cloud with hybrid and client-side AI
Check your understanding
What are the two primary considerations when selecting an AI platform for your application?
When is a server-side managed Service, like Gemini Pro, the best choice for your platform?
What is the main benefit of implementing a hybrid AI system?
